How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?
4.6 (276) In stock
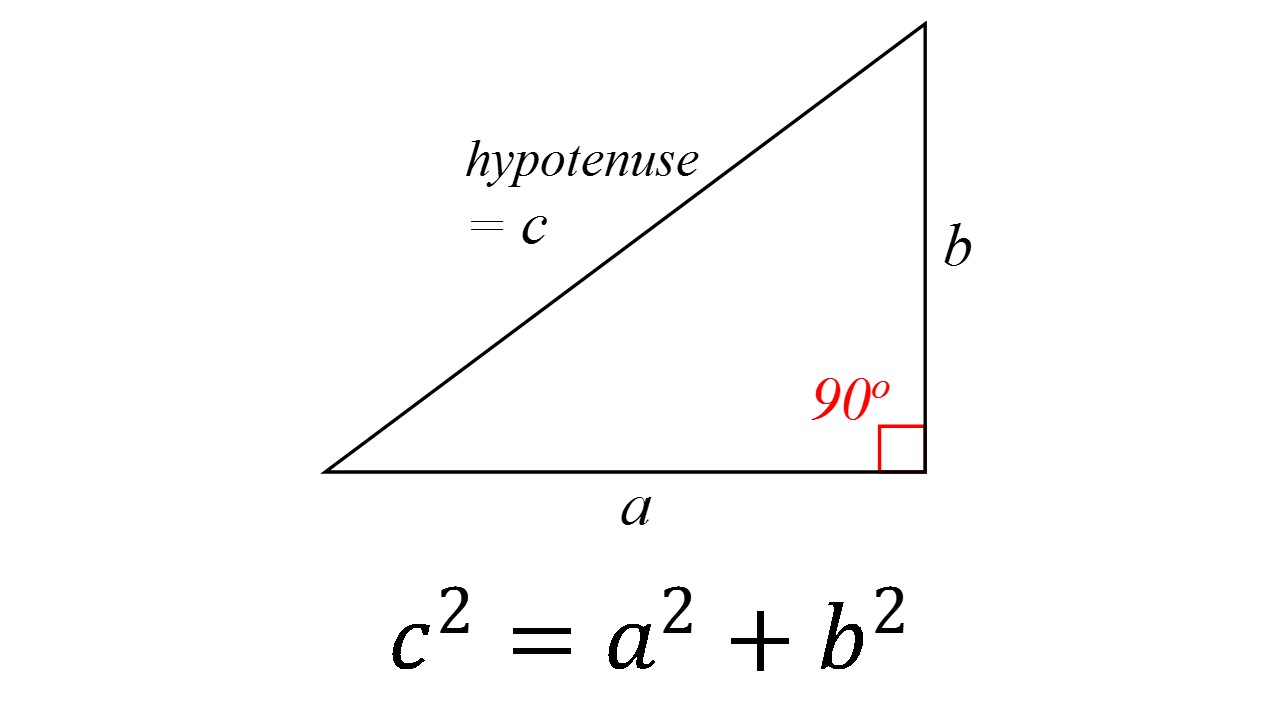
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.

Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines
Pythagoras Theorem - Formula, Proof, Examples, Applications
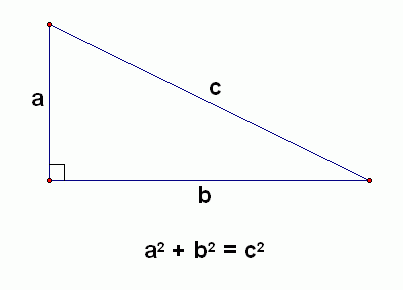
The Pythagorean Theorem - Trigonometry

3-4-5 Triangles, Definition, Rule & Angles - Lesson
How to find the third side of a triangle given two sides - Quora

geometry - Given a 3 4 5 triangle, how do you know that it is a
A triangle has a side of 5 cm, 12 cm, and 13 cm. Why is it a right
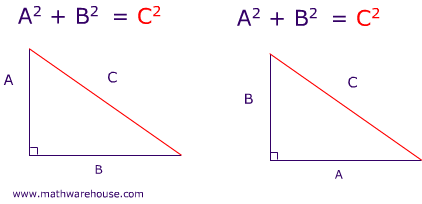
A right triangle's leg is 9 and the hypotenuse is 15, what is the
What is the Pythagorean theorem, and how is it used to solve

How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the
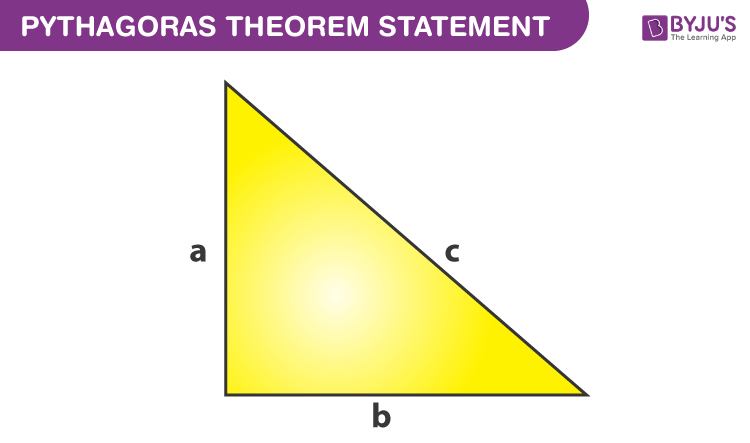
Pythagoras Theorem - Formula, Proof, Examples, Applications

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the missing side of the
Facts about Right Triangles - MathBitsNotebook (Jr)
 Vince Men's Long-Sleeve Thermal Henley Shirt - ShopStyle
Vince Men's Long-Sleeve Thermal Henley Shirt - ShopStyle Best Single-Stack 9mm Handguns for Carry [Top Six List]
Best Single-Stack 9mm Handguns for Carry [Top Six List] lululemon athletica, Bags, Lulu Lemon Tote Bag
lululemon athletica, Bags, Lulu Lemon Tote Bag Non Slip Fabric 150x30cm Black
Non Slip Fabric 150x30cm Black Calf Compression Sleeve for Men & Women (20-30mmHg) - Best Calf Compression Socks for Running, Shin Splint, Calf Pain Relief, Leg Support Sleeve for Runners, Medical, Air Travel, Nursing, Cycling Small /
Calf Compression Sleeve for Men & Women (20-30mmHg) - Best Calf Compression Socks for Running, Shin Splint, Calf Pain Relief, Leg Support Sleeve for Runners, Medical, Air Travel, Nursing, Cycling Small / Fruit of the Loom Women's Breathable Underwear (Regular & Plus
Fruit of the Loom Women's Breathable Underwear (Regular & Plus