SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes inflammatory cytokine activation
4.9 (576) In stock
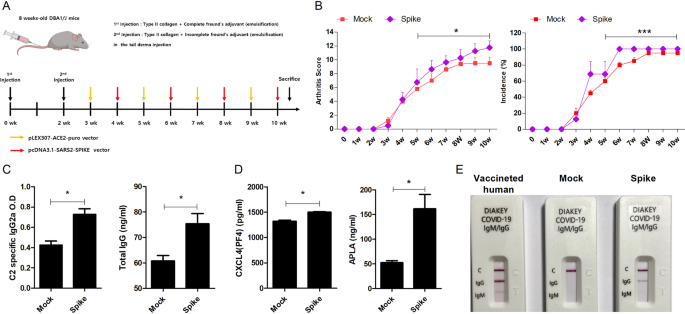
Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induces inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis, which are common symptoms of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effect of COVID-19 on autoimmune disease is not yet fully understood. Methods This study was performed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on the development and progression of RA using a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) animal model. Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were transduced with lentivirus carrying the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein gene in vitro, and the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were measured. For in vivo experiments, CIA mice were injected with the gene encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and disease severity, levels of autoantibodies, thrombotic factors, and inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were assessed. In the in vitro experiments, the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were significantly increased by overexpression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in human FLS. Results The incidence and severity of RA in CIA mice were slightly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in vivo. In addition, the levels of autoantibodies and thrombotic factors, such as anti-CXC chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4, also called PF4) antibodies and anti-phospholipid antibodies were significantly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Furthermore, tissue destruction and inflammatory cytokine level in joint tissue were markedly increased in CIA mice by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Conclusions The results of the present study suggested that COVID-19 accelerates the development and progression of RA by increasing inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis. Video Abstract

SARS-CoV-2 spike protein stimulates IL-6 and soluble IL-6R production.

Effects of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on the development and

CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (RM4-5), Super Bright™ 436 (62-0042-82)
Frontiers Metabolic Implications of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Process in SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis: Therapeutic Potential of Natural Antioxidants
Pyroptotic cell death in SARS-CoV-2 infection: revealing its roles during the immunopathogenesis of COVID-19

IL-17A Monoclonal Antibody (eBio17B7), FITC (11-7177-81)
Why does COVID-19 disproportionately affect older people?
Frontiers Self-DNA driven inflammation in COVID-19 and after

CXCL4/PF4 ELISA DY595 from R&D Systems, a Bio-Techne Brand

SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Accumulation in the Skull-Meninges-Brain Axis: Potential Implications for Long-Term Neurological Complications in post- COVID-19
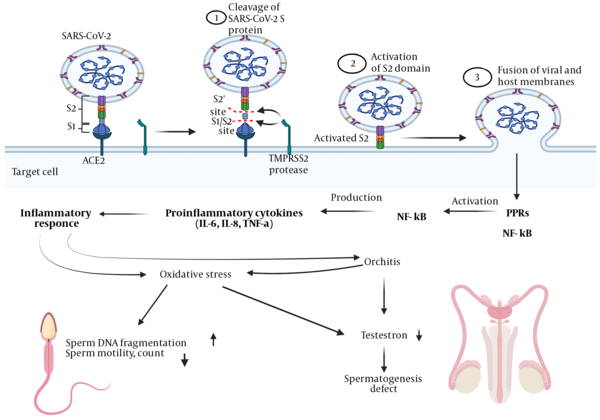
SARS-CoV-2 and Its Implications for the Human Reproductive System: A Review Article, Nephro-Urology Monthly

Mechanisms for the nonantibiotic activities of minocycline and
What is Spike? Definition of the Spike
Voltage Spike & Power Surge, Definition, Causes & Examples - Lesson
spike - Bengali Meaning - spike Meaning in Bengali at english
 Disney Wish: A Complete Guide to What's On Board - WDW Magazine
Disney Wish: A Complete Guide to What's On Board - WDW Magazine Bras N Things Castille Push Up Bra - Lilac - PURPLE - ShopStyle
Bras N Things Castille Push Up Bra - Lilac - PURPLE - ShopStyle Women's Active Maximum Support Extreme Control Sports Bra
Women's Active Maximum Support Extreme Control Sports Bra DANG SOFT SERVE ICE CREAM - 211 Photos & 171 Reviews - 2211 Oneida St, Denver, Colorado - Ice Cream & Frozen Yogurt - Yelp
DANG SOFT SERVE ICE CREAM - 211 Photos & 171 Reviews - 2211 Oneida St, Denver, Colorado - Ice Cream & Frozen Yogurt - Yelp Thigh Split Beaded Coffee Sheer Tulle Evening Gown - Xdressy
Thigh Split Beaded Coffee Sheer Tulle Evening Gown - Xdressy Demi-Gods and Semi-Devils – Review – Drama Delight
Demi-Gods and Semi-Devils – Review – Drama Delight