1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only. - ppt download
4.8 (69) In stock

3 Slope Stability In slope stability analysis we determine the Factor of Safety as a ratio of resisting forces to driving forces F s = Resisting / Driving Theoretically, any slope with a Factor of Safety less than one will fail and any slope with a factor of safety greater than one will not. Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data.
1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only
2 Slope Stability In general you have: Driving Force – Weight of Slope Resisting Force – Strength of soil along slip surface Buttress at toe W c
Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data..
4 Slope Stability Example of Circular Slip Surface (from geoslope software) Circular slip surfaces often used in analysis as the most likely approximated shape of the failure surface
5 Slope Stability Non circular slip surfaces can also be analyzed
Now: W n sin α (driving) N= W n cos α T r = shear face = c’ + F ’ tan φ’ (resisting) W n sinα W n cos α α.
7 Slope Stability Performing this analysis on each slice and then summing the components from each slice F s = Σ (c L + W cos α tan φ) / Σ (W sin α )
8 Slope Stability This analysis is very conducive to a tabular solution WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ8 + 9 F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)
9 Slope Stability - Example Each box is 5’ x 5’ * = 120 pcf c = 300 psf φ = 32 o
10 Slope Stability - Example First, Find the areas for each slice A1 A2 A3 A4
11 Slope Stability WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)

/12/3544628/big_thumb.jpg

Slope Stability

Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Federal Register :: 2017 and Later Model Year Light-Duty Vehicle Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards
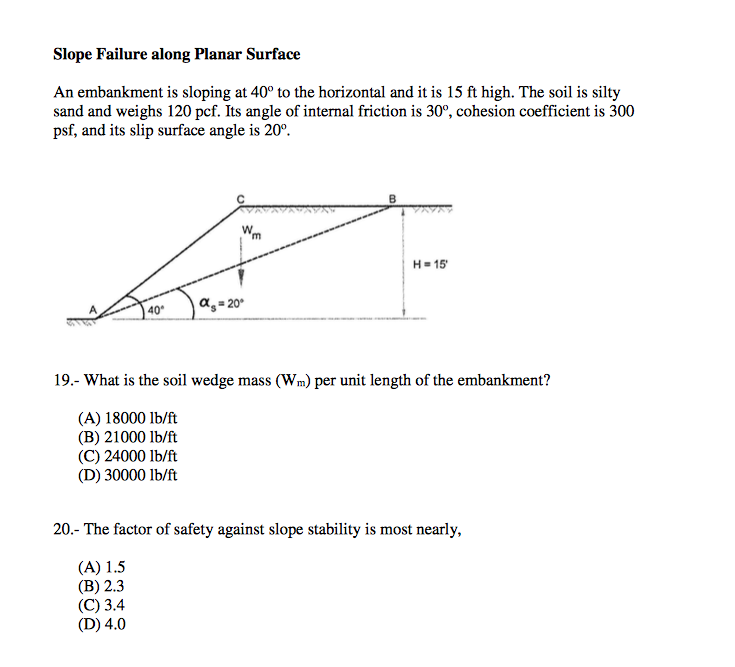
Solved Slope Failure along Planar Surface An embankment is

A practical procedure for the back analysis of slope failures in closely jointed rock masses - ScienceDirect

2022 Scientific Research in School by Barker College - Issuu

Soil–rock mixture slope stability analysis by microtremor survey and discrete element method

Ch10-Slope Stability Examples, PDF, Soil Mechanics

images./33/8194036/slides/slide_5.j
Rayleigh–Taylor unstable condensing liquid layers with nonlinear effects of interfacial convection and diffusion of vapour, Journal of Fluid Mechanics

A practical procedure for the back analysis of slope failures in closely jointed rock masses - ScienceDirect
Solved A ball is released from rest on a no-slip surface, as
Synthetic Ice Surface Conditioner - 5 Gallons – PolyGlide Ice
 MOUNT JULIET ESTATE, AUTOGRAPH COLLECTION - Updated 2024 Prices & Hotel Reviews (Ireland/Thomastown, County Kilkenny)
MOUNT JULIET ESTATE, AUTOGRAPH COLLECTION - Updated 2024 Prices & Hotel Reviews (Ireland/Thomastown, County Kilkenny) GapFit Eclipse Low Support Square-Neck Sports Bra
GapFit Eclipse Low Support Square-Neck Sports Bra Clothing & Shoes - Socks & Underwear - Bras - Rhonda Shear Seamless Crochet Back Ahh Bra (2-Pack) - Online Shopping for Canadians
Clothing & Shoes - Socks & Underwear - Bras - Rhonda Shear Seamless Crochet Back Ahh Bra (2-Pack) - Online Shopping for Canadians STKOOBQ Valentines Day Sexy Thong Panties Womens Low Rise Lace Panties Comfy Thongs Sweat Outfit for Women after (Black, S) : Clothing, Shoes & Jewelry
STKOOBQ Valentines Day Sexy Thong Panties Womens Low Rise Lace Panties Comfy Thongs Sweat Outfit for Women after (Black, S) : Clothing, Shoes & Jewelry Bare The Smooth Multiway Strapless Bra 34DDD, Hazel
Bare The Smooth Multiway Strapless Bra 34DDD, Hazel- Lore Larroza Regalos Personalizados - Agenda para Mujeres Jóvenes
