Virial coefficients: empirical approx. of the compression factor
4.8 (639) In stock


Mind the Gap Pt 1 – Equations of State in Oil/Gas/Petro… (6 minute read)
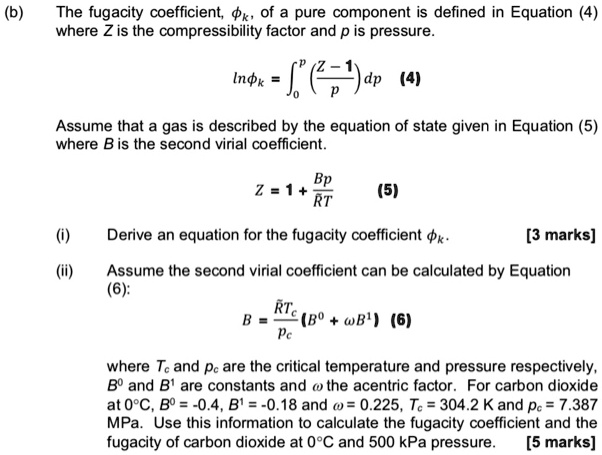
SOLVED: The fugacity coefficient of a pure component is defined in Equation 4, where Z is the compressibility factor and p is pressure. nk = 4 Assume that a gas is described
Vacancy defects impede the transition from peapods to diamond: a neuroevolution machine learning study - Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D3CP03862A
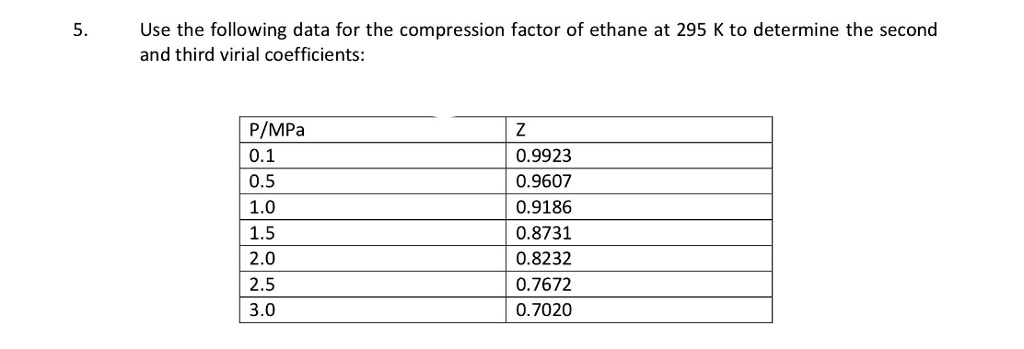
SOLVED: Use the following data for the compression factor of ethane at 295 K to determine the second and third virial coefficients: PIMPa 0.1 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 0.9923 0.9607 0.9186 0.8731 0.8232 0.7672 0.7020

DOC) Computation of the Compression Factor and Fugacity Coefficient of Real Gases

A generalized correlation for the second virial coefficient based upon the Stockmayer potential

1 Gases and fluids

Van der Waals Theory of Imperfect Gases

An Equation for Prediction and or Correlation of Second Virial - GENERAL RESEARCH An Equation for - Studocu

Third virial coefficient as a function of temperature for Q 2 ¼ 4 and

Solved Answer the following questions briefly: 1. Reported
COMPRESSIBILITY factor Z, Using P and v in 3 Minutes!
Summary of Equations used to evaluate compressibility factor, z
Math cad compressibility factor, z, of real gas using the redlich
- Women - Underwear: Seamless Front Buckle Support Bra 2 in 1 Posture Corrector Bra Back Shaper (11.99 EUR)
 Elegance® 36 - Ambiance®
Elegance® 36 - Ambiance® (8) Pack VELCRO® BRAND Fastener Morale HOOK PATCH USA Patches 3.75x1
(8) Pack VELCRO® BRAND Fastener Morale HOOK PATCH USA Patches 3.75x1 Atlanta Braves Shirt by Alberto Cerriteno - Issuu
Atlanta Braves Shirt by Alberto Cerriteno - Issuu Manduka Uphold Recycled Foam Block - Be Bold Blue - PROPS
Manduka Uphold Recycled Foam Block - Be Bold Blue - PROPS Buy Quality Macy - Braided Jumbo Box Braids Wig from RealWigs
Buy Quality Macy - Braided Jumbo Box Braids Wig from RealWigs
