Compression Factor Exam Problem using Molar Volumes - Fully Explained!
4.5 (731) In stock

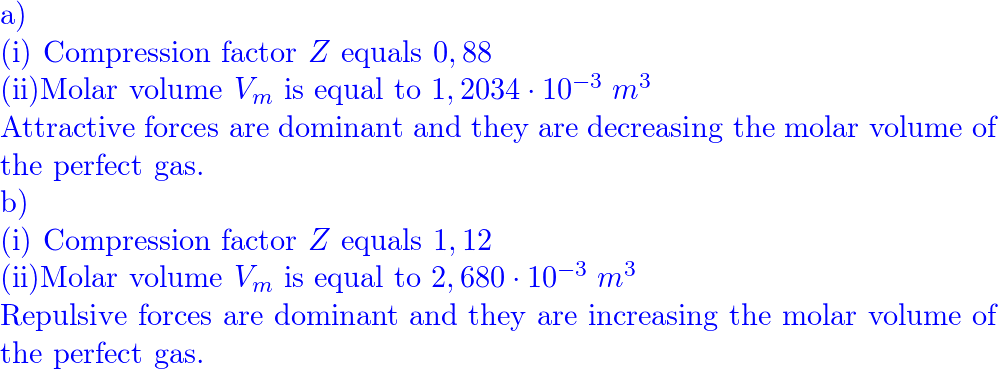
a) A gas at 250 K and 15 atm has a molar volume 12 per cent

Physical Chemistry The Compression Factor (Z) [w/1 example]

Compression Factor Exam Problem using Molar Volumes - Fully Explained!

Compressibility Factor - an overview

Solved 2) Write a computer program to calculate molar volume
Text: Physical Chemistry, 7th Edition, Peter Atkins and J. de Paula - ppt download

Systematic study of paracetamol powder mixtures and granules tabletability: Key role of rheological properties and dynamic image analysis - ScienceDirect

Thermodynamics

Internal Energy Practice Problems

How to Calculate a Final Temperature Using the Ideal Gas Law Equivalency, Physics

Isothermal Compression - an overview

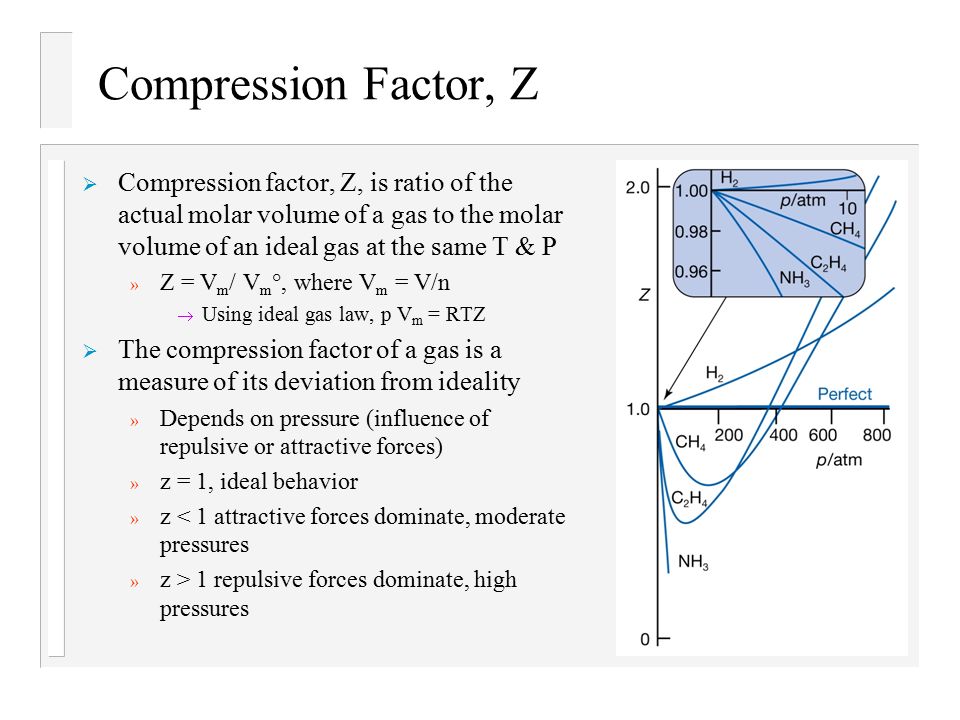
Explain how the compression factor varies with pressure and

2013 General Chemistry I 1 Chapter 4. THE PROPERTIES OF GASES 2013 General Chemistry I THE NATURE OF GASES THE GAS LAWS 4.1 Observing Gases 4.2 Pressure. - ppt download
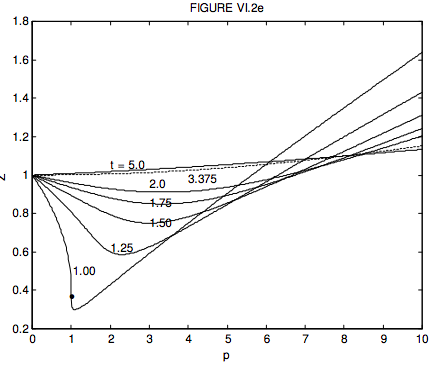
6.3: Van der Waals and Other Gases - Physics LibreTexts

Compressibility Factor of Gas, Overview, Equation & Chart - Lesson
COMPRESSION AND EXPANSION OF GASES – Chemical Engineering Projects
a) Suppose that $10.0\ \mathrm{mol}\ \mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm
the compression factor one mole of a vander waals gas 0 C and 100