Ulnar Nerve Anatomy and Function The Ulnar nerve is
5 (366) In stock

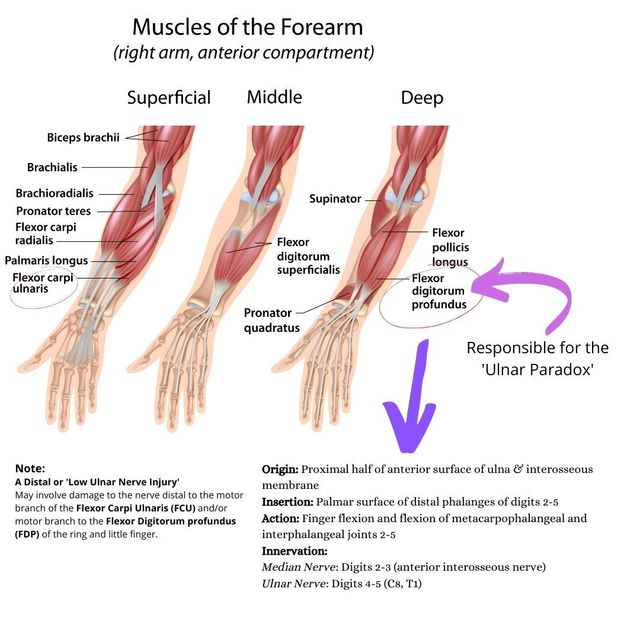
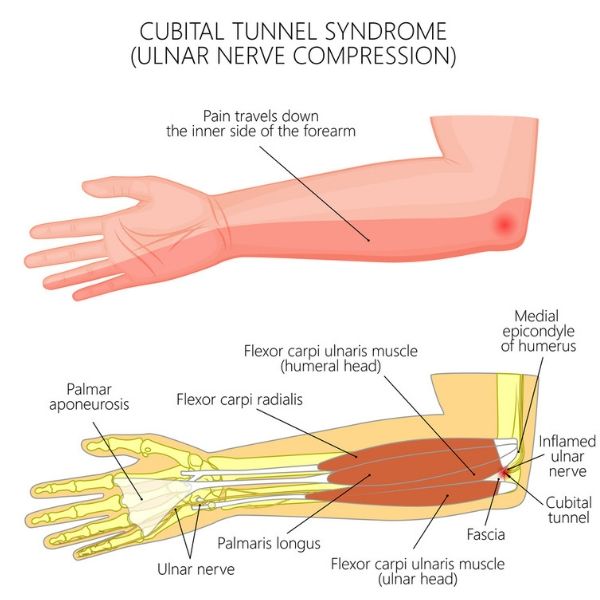
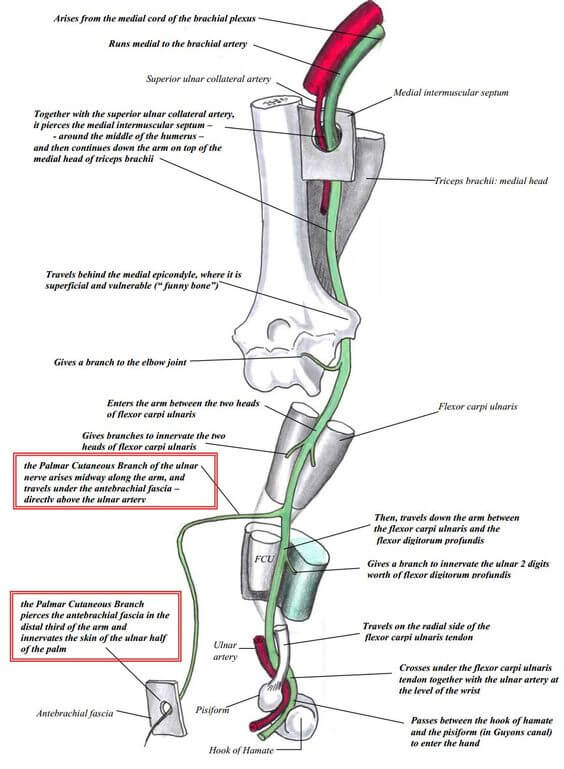
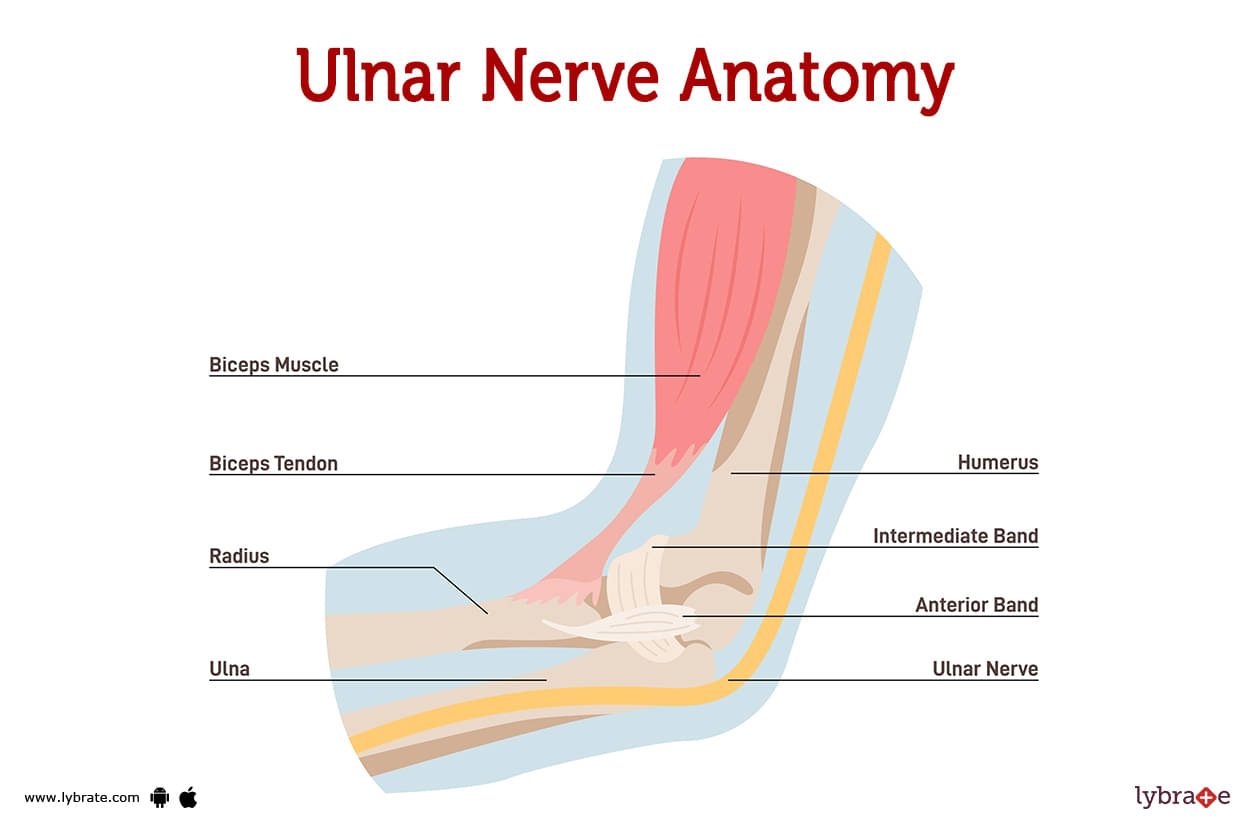
Ulnar Nerve Anatomy and Function The Ulnar nerve is the nerve of hand power and control. It is the post axial nerve and innervates the intrinsics of the hand (minus the LOAF of the median nerve). It provides sensation to the Ulnar side of the palm and dorm of the hand and the little and ulnar half of the ring finger. It powers the deep flexors and lumbricles of these fingers too. It is formed by the C8 and T1 roots via the lower trunk and the medial cord. Here the sensory nerves of the inner arm and forearm leave and the Ulnar nerve commences. It has no branches in the arm until after it leaves the cubital tunnel. When clinically assessing the Ulnar nerve remember: • it does not innervate the inner arm or forearm sensation • Compression can occur at many points along the course of the neurones from TOS to the hand. • Clawing is due to intrinsic extrinsic imbalance. • The ulnar paradox is that in a high lesion the clawing is less severe as the extrinsics are reduced in power as well as the intrinsics. by Dr. Tom Quick @TJQPNI via orthohub.xyz @OrthohubXYZ #Ulnar #Nerve #Anatomy #diagnosis #neurology #orthopedics

Patient Education Article - Columbia Orthopaedic Group - Patient
Nerve Entrapment, Injury and Neuropathy; Ulnar Nerve
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment, Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
The Ulnar Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - TeachMeAnatomy
Ulnar nerve - Course and Innervation

Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Elite Sports Medicine + Orthopedics
Ulnar Nerve (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments

Brachial Plexus Injury, Living With Paralysis
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ulnar-nerve-2/arELS1HpCVvGozLThoofZA_N._ulnaris_02.png)
Ulnar nerve: Origin, course, branches and innervation
Ulnar nerve entrapment - Wikipedia
Ulnar nerve dysfunction Information
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Without injection Or surgery
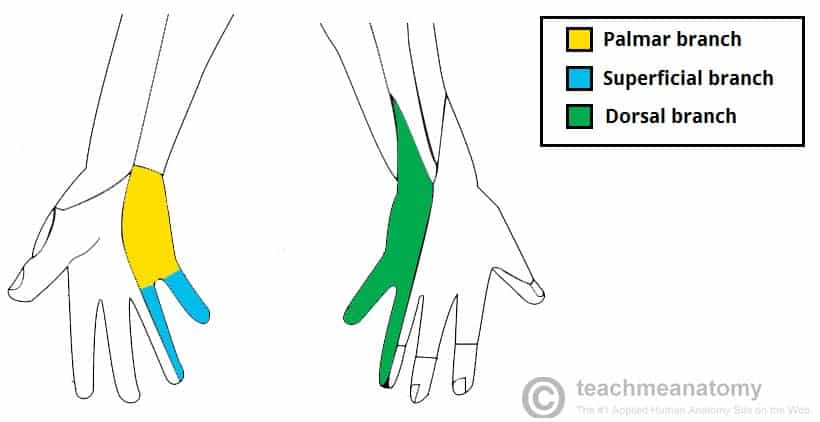
Ulnar Nerve Compression in Guyon's Canal
Ulnar Neuropathy – Peripheral Nerve Conditions – The American
 Large Round Dining Tables Seats 10 - Foter Large round dining table, Round dining room, Round dining room table
Large Round Dining Tables Seats 10 - Foter Large round dining table, Round dining room, Round dining room table KND 6418N WINGS FLUFF AND POLYMER UNDERPAD EXTRA HEAVY ABSORBENCY
KND 6418N WINGS FLUFF AND POLYMER UNDERPAD EXTRA HEAVY ABSORBENCY Body contenitivo sempllice liscio ottimo per tutte le occasioni Tenuta media
Body contenitivo sempllice liscio ottimo per tutte le occasioni Tenuta media Lenovo Yoga 7 14-inch and Yoga 7 16-inch variants get refreshed to
Lenovo Yoga 7 14-inch and Yoga 7 16-inch variants get refreshed to Waistband Logo Mini Shorts in neutrals - Palm Angels® Official
Waistband Logo Mini Shorts in neutrals - Palm Angels® Official Audrey Harness Bra, Cone Bra, Black Pvc Bullet Bra, Halter Top
Audrey Harness Bra, Cone Bra, Black Pvc Bullet Bra, Halter Top