10.9: Real Gases - Deviations from Ideal Behavior - Chemistry LibreTexts
4.7 (72) In stock
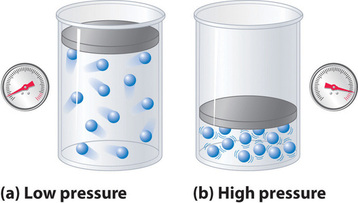
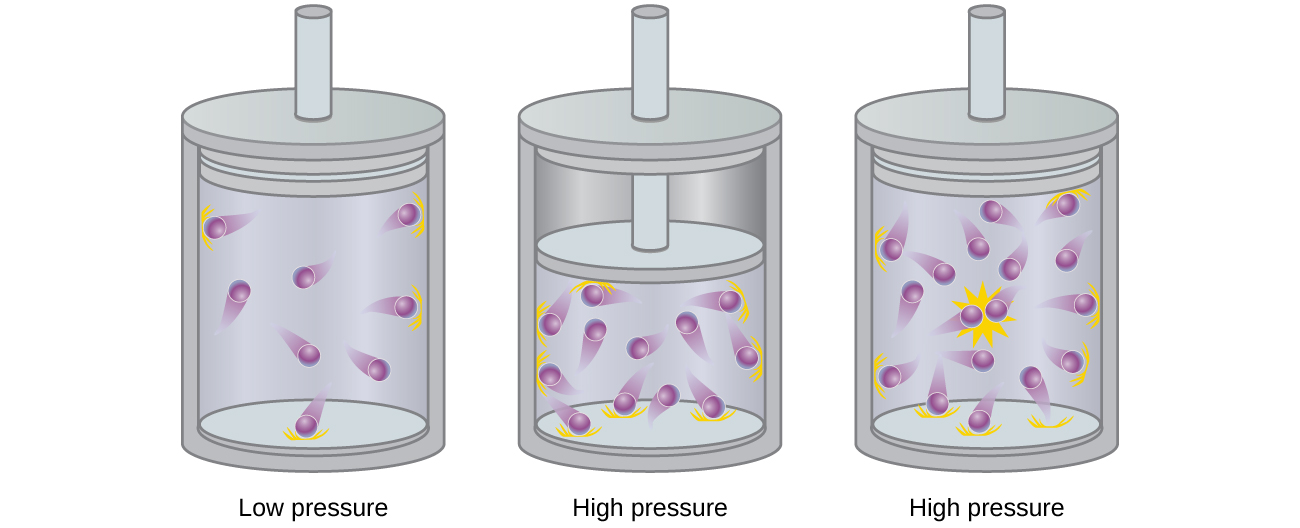
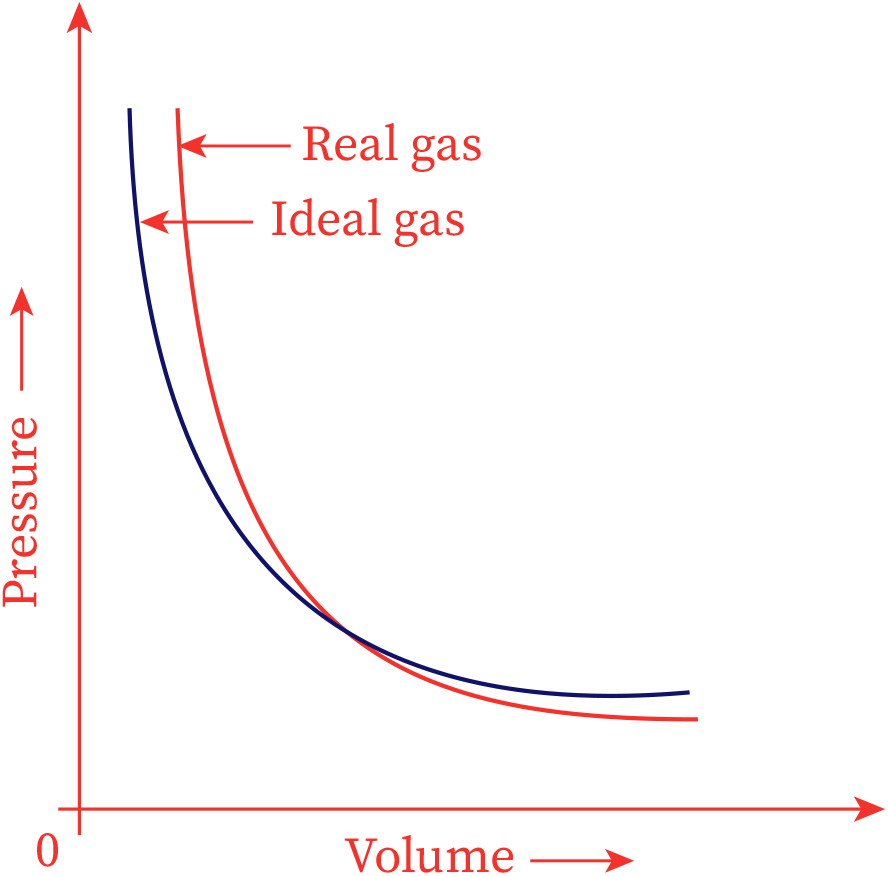
No real gas exhibits ideal gas behavior, although many real gases approximate it over a range of conditions. Gases most closely approximate ideal gas behavior at high temperatures and low pressures. …
No real gas exhibits ideal gas behavior, although many real gases approximate it over a range of conditions. Gases most closely approximate ideal gas behavior at high temperatures and low pressures. Deviations from ideal gas law behavior can be described by the van der Waals equation, which includes empirical constants to correct for the actual volume of the gaseous molecules and quantify the reduction in pressure due to intermolecular attractive forces.
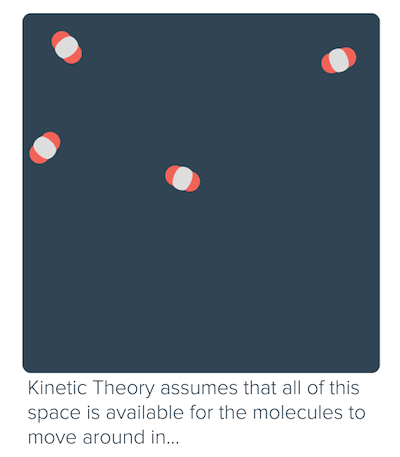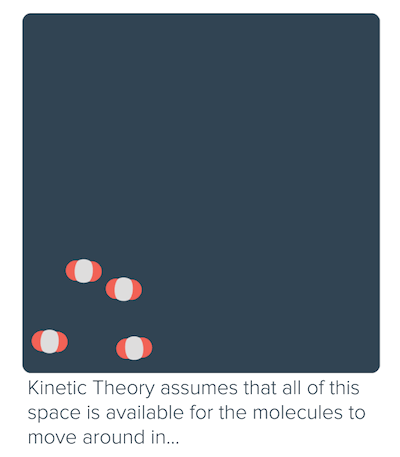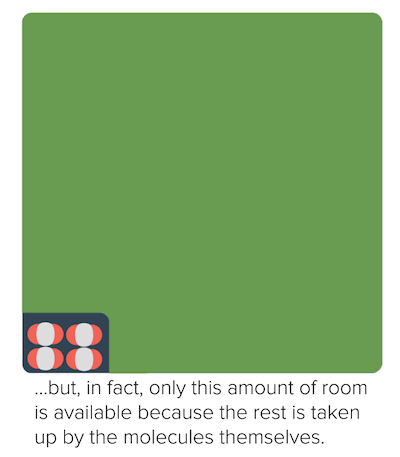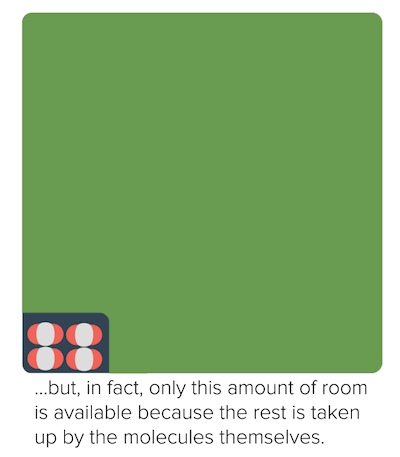
Non-ideal behavior of gases (article)
How to predict which of the given gases is more non-ideal - Quora

Deviations from Ideal Gas Law Behavior

Non-ideal behavior of gases (article)
1.1: Non-Ideal Gas Behavior - Chemistry LibreTexts
1. An unspecified ideal gas at 10°C and 100kPa occupies a volume of 2.5 m³. (a) How many moles does this gas have? (b) If the pressure and temperature are raised three

10.9: Real Gases - Deviations from Ideal Behavior - Chemistry LibreTexts

Deviations from the Ideal Gas Law, Study Guides, Projects, Research Chemistry

Chapter 10 - Gases Prof. Dr. Nizam M. El-Ashgar - ppt download

Behaviour of Real Gases, PDF, Gases

Real gases: Deviations from ideal behavior, AP Chemistry
Ideal and Real Gases

Modeling of H2S solubility in ionic liquids using deep learning: A chemical structure-based approach - ScienceDirect

Solved Which statement about real vs. ideal gases is not
Under Armour mens Hovr Highlight Ace
How to Lower Cortisol: Foods and Activities to Try
 Genie Style Bra XL/1XL Black Nylon Spandex Removable Pad Shapewear Seamless Bra - Helia Beer Co
Genie Style Bra XL/1XL Black Nylon Spandex Removable Pad Shapewear Seamless Bra - Helia Beer Co Medias largas de malla para mujer, estilo de red de
Medias largas de malla para mujer, estilo de red de Hamstring Injuries Advanced Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine
Hamstring Injuries Advanced Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Rib and Roast Rack - Big Green Egg
Rib and Roast Rack - Big Green Egg Pantalón de Tela Stretch CODIGO 981
Pantalón de Tela Stretch CODIGO 981- Titan Signature Gold Wrist Wraps - IPF Approved Powerlifting
